Thank you for visiting the AUSTRALIA HP Store
-
Contact Us
CONTACT USCall us
- Sales
- 1300 540 516
- Technical support
- 13 23 47
Exc. public holidays
Chat with us- Our specialist are here to help
- Live Product Demo
- Sales
- 61288061500 (WhatsApp)
-

- Post Sales
- 61288061700(WhatsApp)
Exc. public holidays
Live product demo
Submit feedback We value your opinion! - My Account
Edge Computing: Revolutionising Data Processing

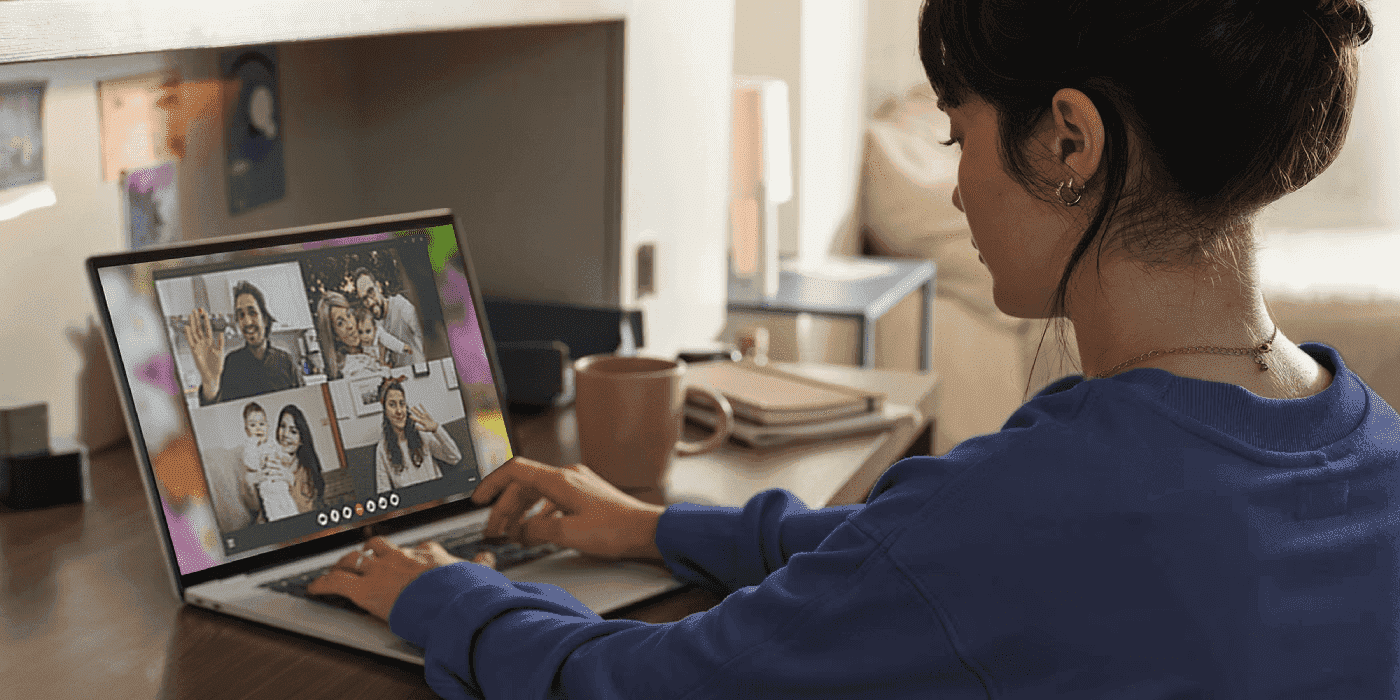
Recently, the way data is processed has started to evolve, with the concept of edge computing gaining traction.
Edge computing is a form of computing where data is processed close to where it’s generated. It’s done on the edge of a network or by devices that have the computing power necessary to collect, process and act on the data with relative independence.
Before the advancement of edge computing, cloud computing was the dominant approach. Cloud computing centralises the data, transferring it from where it was generated and processing it in large data centres. It is a cost-effective approach that allows for the efficient sharing of resources but may soon be eclipsed by edge computing.
How edge computing works
Edge computing involves a few different components that work together to provide efficient processing.
Edge devices
An edge device is a physical item at the endpoint of a network, connecting the digital network to the outside world. These devices generate data, provide feedback and take directions from the end user. They can monitor and manage machinery, capture observable events as data, and send and receive information. A local edge server processes data from the device rather than sending it to a central cloud server, like with cloud computing.
The complexity of an edge device can vary immensely and encapsulates every item that’s part of the Internet of Things (IoT). Edge devices include sensors, mobile phones, scanners, automated machinery, scientific instruments, medical equipment and autonomous cars.
Edge servers and gateways
Edge servers and gateways help facilitate edge computing. Edge servers are computers situated away from a centralised data centre. These PCs can connect the edge device to the network, connect to another edge service and act as a gateway if needed. When an edge server acts as a gateway, it becomes the point of connection linking the edge processing system to a larger network or the cloud.
Real-time data processing
Edge computing is naturally suited for applications that require minimal latency. Since the data is being processed and analysed as close to the source as feasibly possible, edge computing is faster than cloud computing, offering an advantage for time-sensitive applications.
The real-time data processing that edge computing facilitates is essential for advancing technology in fields where fast judgements critically impact safety, outcomes and efficiency. This includes automated vehicles, healthcare applications and smart city management.
Applications of edge computing
There are several applications for edge computing, from smart watches and voice assistants to fleet management, telecommunications and predictive maintenance of complex machinery. As technology continues to develop, the list of applications for edge computing is likely to rise. But for now, here are five important areas currently utilising edge computing.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to everyday physical items connected to the internet, including light bulbs, televisions and smart watches. These physical devices receive input information from the user and produce data. Since edge computing collects and processes data at the edge of the network rather than a central data centre, it decreases communication latency and increases response times. This results in a better user experience.
Smart cities
Recent patterns in human migration show that an increasing percentage of the global population is choosing to live in urban areas. This puts a strain on the infrastructure that requires smart solutions to solve.
The idea of a smart city is to use real-time data and analytics from devices, including sensors, cameras and roadway signals, to ensure that resources and services are being used as efficiently as possible, with the greatest benefit to citizens. Employing edge computing in this context allows for faster data processing and analysis of citywide systems, including energy grid optimisation, surveillance camera detection, parking management, street light optimisation and traffic management.
Manufacturing and industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, which began during the 1990s and is ongoing today. This revolution centres around the rise of automated systems and data-driven manufacturing processes. In recent times, it has given rise to the concept of a Smart Factory.
In many modern factories, manufacturing machinery is networked, sending and receiving data in real-time that’s processed using edge computing. The data comes from several sources, including sensors, and can provide information that helps identify anomalies, maximise productivity and efficiency, and prevent maintenance issues, resulting in less downtime for the plant.
Healthcare
The health industry has seen great potential in edge computing in healthcare systems around the globe. It decreases strain on the overall network, and the real-time processing capabilities can significantly impact patient care.
Using edge computing, medical staff can remotely monitor vials, automate care delivery, and use AI diagnostic tools to help improve treatment times. The opportunity to get real-time imaging and patient analytics makes it easier for doctors to triage, diagnose and treat patients, which in turn can result in improved outcomes.
Autonomous vehicles
Around the world, there is great interest in autonomous vehicles for personal and commercial use. Edge computing is essential to this development as low latency responses are critical. The vehicles must be able to swiftly and efficiently process sensor data to assess the surrounding environment, identify objects and obstacles, estimate distances with relatively high accuracy, accelerate appropriately, and make instantaneous judgments. Without edge computing, autonomous technology faces challenges before it can be safely deployed.
Benefits of edge computing
Reduced latency
Latency refers to the amount of time that passes between sending and receiving data. The distance between where the data is produced and where it is processed are significant factors that influence latency. Reducing latency is one of the key benefits of using edge computing and edge devices. The decentralised model expands the number of locations for processing, putting it closer to the origin point of the data and reducing the load on the networks.
Enhanced security
With cloud computing, data is transmitted across external networks, which can create a security breach. Edge computing limits how far the data needs to travel, keeping sensitive information closer to the point of creation. This makes it easier to maintain control of the data and decreases the likelihood of a data breach. For some industries, including the financial sector, healthcare industry, telecommunications and government sector, this is of critical importance.
Improved efficiency
When cloud computing is used, huge volumes of raw data are transferred between the point of origin and the central processing infrastructure. This can result in network and bandwidth congestion, which decreases efficiency. Edge computing systems are more independent, and decentralised transfers mean less traffic through the main network. The independence also has the added benefit of allowing some systems to continue working in remote locations where network access is inconsistent or unavailable.
Cost-effectiveness
Compared to cloud computing, edge computing can be a more economical method in situations where sending large volumes of data result in higher network expenses. It can also be a more scalable solution, as each additional new device can process its own data rather than putting increased strain on the cloud infrastructure.
Future trends in edge computing
Growth and adoption projections
Currently, the edge computing market is growing exponentially as more and more organisations realise the value of process data at the source. This is expected to continue as the advantages of this computing become evident to a greater audience.
Emerging technologies in edge computing
Advancements in edge computing technologies are happening in a range of areas. Some of the most exciting involve cutting-edge technology that was not possible only a few decades ago:
-
Artificial intelligence
-
Augmented reality
-
Autonomous robots and vehicles
-
Drone detection
-
Environmental condition monitoring
Summary
Edge computing represents a positive shift in how data is processed. The benefit of having the data processing take place closer to the source can not be understated. It plays a significant role in making further technological advancements possible and is likely to become the dominant form of computing.
- Sales
- 1300 540 516
- Technical support
- 13 23 47
Exc. public holidays
- Our specialist are here to help
- Live Product Demo
- Sales
- 61288061500 (WhatsApp)
-

- Post Sales
- 61288061700(WhatsApp)
Exc. public holidays
Live product demo








