Thank you for visiting the AUSTRALIA HP Store
-
Contact Us
CONTACT USCall us
- Sales
- 1300 540 516
- Technical support
- 13 23 47
Exc. public holidays
Chat with us- Our specialist are here to help
- Live Product Demo
- Sales
- 61288061500 (WhatsApp)
-

- Post Sales
- 61288061700(WhatsApp)
Exc. public holidays
Live product demo
Submit feedback We value your opinion! - My Account
How to Effectively Manage and Organize Files in the Cloud

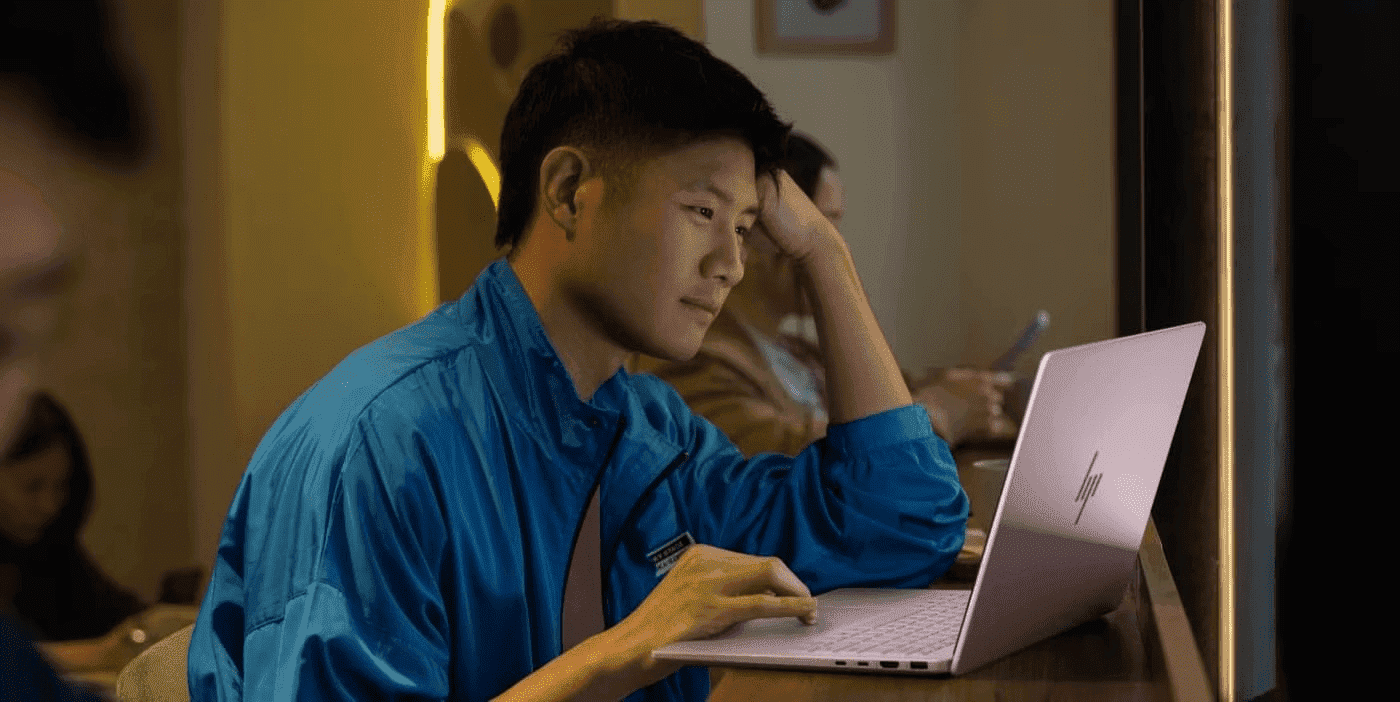
Did you know the average employee spends 9 hours creating files, 3 hours organising them, and 5 hours looking for the right one? That’s nearly 50% of your work week! Just by learning some tips and tricks on digital workspace management, you can regain precious time and boost your productivity at work.
Cloud file organisation solutions have made sharing, backup, and security more convenient for teams. You no longer have to worry about losing hours of work just because your laptop crashed. However, files accumulating across various cloud storage services can make finding a critical document from months ago feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. Disarray can pose security risks and lead to costly data redundancies.
This article explores top strategies for efficiently managing files in the cloud, helping you streamline your workflow and regain your sanity!
Establish Effective Folder Structures
A systematic folder structure provides a framework for file organisation clarity. Everyone knows where to look for specific information and where to store new data. However, you must define naming conventions and hierarchies early on.
For example:
-
Client and Category: Client Name/Project Category/FileName
-
Date and Event: Year/Month/Event/FileName
-
Department and Type: Department/Document Type/FileName
The main thing is to ensure consistency between projects and team members. Software that automatically creates directory structures is more reliable than manual processes that introduce human error.
Implement File Naming Conventions
Consistent and descriptive file naming conventions facilitate easy file retrieval. Consider these tips:
-
Start with the most essential descriptor in the file name to identify a file's content at a glance.
-
Stick to alphanumeric characters as special symbols like slashes, colons, and asterisks cause errors on some cloud platforms.
-
Choose whether to use camelCase, PascalCase, or under_scores and stick to it.
-
Include a version number at the end of the file name, such as v1, v2, etc.
-
Refrain from using vague labels like 'final' or 'new' that can become confusing over time, especially when multiple versions exist. If chronological sorting is necessary, include the date in the file name (formatted as YYYYMMDD to avoid date format confusion in global teams).
While descriptiveness is critical, aim for balance so excessively long names don't cause display issues.
Utilise Tags and Metadata
Metadata refers to data about data, such as the date a file was created, the author, or the type of content it contains. Tags are customisable labels you can apply to files and folders to categorise them as needed. Both are important for organisation and searchability. They also make using the same files easier for automation technology and humans.
Strategies include:
-
Establish a standard set of tags relevant to your projects and team.
-
Define a standard metadata schema that requires filling out specific fields for each file type.
-
Organise training sessions to help standardise practices across the team.
Consider a hierarchical structure for larger projects where more specific sub-tags refine broad tags. For example, a broad tag like “Marketing” can have sub-tags like “Q1 Campaigns” and “Social Media.”
As projects evolve, the relevance of certain tags may change. Schedule regular reviews of your tagging strategy to ensure that it continues to meet your organisational needs.
Leverage Version Control Practices
Version control is a systematic method for managing changes to files. It lets you preserve the history of document changes and revert to previous versions if needed. It prevents updates by one team member from overwriting essential changes made by another.
Many cloud storage platforms offer built-in version control features that automatically save file revisions. Users can view previous versions, restore them if necessary, and understand the chronology of changes. See the summary below.


For more complex projects, dedicated version control systems like Git can be used, even for non-code files. You can also use tags within your version control tools to categorise versions by milestones or project phases and quickly locate the most relevant version.
Securely Maximise Collaboration
Many cloud storage services provide features that allow multiple users to edit documents simultaneously and see each other’s changes. They also enable real-time collaboration, commenting, and task assignment directly within documents. For example, team members can leave feedback, ask questions, and point out revisions directly on the file. This keeps all relevant discussions in context and easily accessible. Teams can centralise communication and reduce the need for back-and-forth emails or meetings.
However, security is essential for collaboration to be effective. Team members must have suitable access and permission levels for their needed files. Implementing robust security measures also safeguards your data and builds trust with clients and stakeholders.
-
Encryption: Encryption is the first line of defence in protecting your file data’s confidentiality and integrity. Most reputable cloud service providers offer encryption at rest, which means your files are encrypted on the server. However, you must ensure that files are encrypted even during transmission over your network or if shared via email and chat.
-
Access Permissions: Define roles and permissions based on the least privilege principle so individuals can only access the files necessary for their roles. Generate shared links for files or folders when you need to give someone access without granting them broader permissions to the entire directory. You can customise the links with expiration dates and download limits for more control.
-
Multi-factor Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication that asks for more evidence than just a password when verifying user identity.
Automate File Organisation Tasks
Automating repetitive file organisation tasks saves time and reduces the likelihood of human error. Cloud file management systems perform many tasks out of the box — for example, folder synchronisation across devices, automatically uploading file changes, notifying other members of changes made, and so on.
You can also use additional tools to automate complex file admin tasks and workflow integrations. For example, the tool triggers the creation of folders in your cloud storage with predefined naming conventions and access permissions when a new project is registered in your project management tool.
Some popular file automation tools:
-
Tabbles and Files.com: Automate the tagging of files based on predefined rules.
-
Acronis and Backblaze: Offer scheduled backups that ensure data integrity and quick recovery in case of data loss.
-
Zapier and Microsoft Power Automate: Connect various apps and services, automatically renaming, reformatting, and moving files between software systems.
Implement Backup and Recovery Strategies
Backup involves making copies of data to restore the original after a data loss event. Recovery is the process of restoring lost data from the backup. Even though cloud file systems automatically back up in the cloud, there is a good chance that the cloud account itself is compromised or corrupted with ransomware. Having a separate file store copy is critical for maintaining business continuity.
A time-tested strategy is the 3-2-1 backup rule:
-
Keep at least three copies of your data.
-
Store these copies on two different media.
-
Keep one backup copy offsite.
Just as with your primary data, ensure that backups are encrypted and access is tightly controlled.
Base the frequency of backups on how frequently the data changes and how critical it is to operations. For most businesses, daily backups are recommended. Utilise tools that support automated backups to reduce the need for manual intervention and minimise the risk of missed backups.
Test your recovery process regularly as part of your routine disaster recovery plans to ensure you can quickly restore data from your backups.
Conclusion
The strategies outlined above provide a starting point for file storage management. We encourage you to review your current practices and integrate what is missing. AI and machine learning in cloud file management will likely further revolutionise how you store, retrieve, and secure your files. Proactive file management will better position you to leverage advancements and maintain a competitive edge in the AI era.
- Sales
- 1300 540 516
- Technical support
- 13 23 47
Exc. public holidays
- Our specialist are here to help
- Live Product Demo
- Sales
- 61288061500 (WhatsApp)
-

- Post Sales
- 61288061700(WhatsApp)
Exc. public holidays
Live product demo








